Home page
» GEOGRAPHY
» Physical Geography
» The Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea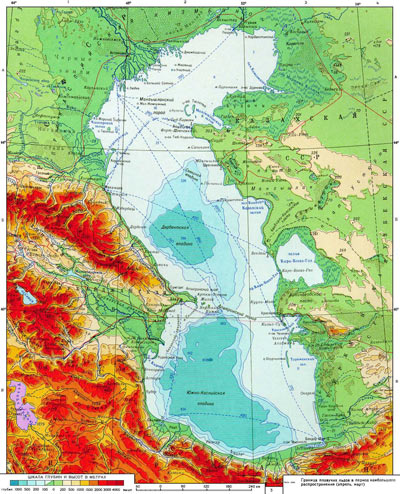 The Caspian Sea
The oldest information about the Caspian Sea is found in the ancient Assyrian clay vessels, where it was called as the South Sea. In works of Greek historian and geographer Hekatey Miletski (VI century BC) this seas was named as Kaspiy and Hirkan. Both names were used by Herodotus (V century BC), too. In ancient Russian manuscripts the Caspian Sea was named as Blue (taken from Mongols-Turks), Kharazm (connected with Kharazm state located in valley of Amudarya River and stretching from the Caspian Sea), Khvalin, Derbent, etc. The people living around the Caspian Sea gave different names to this sea, too, for example, Russians-Khvalin, Tatars-White Sea, the Turks - the Small Sea, Chinese- Si Hay, that is, the Western sea. In general, at different times, different nations gave about 70 names to the Caspian Sea.
 Fauna
The diversity of fauna and flora of the Caspian Sea is unique. It is distinguished from other sea and lakes. Fauna of the Caspian Sea differs from the typical marine fauna. Three reserves had been created in the Caspian Sea coastal zone: the Gizilagach, Astrakhan in Russia, Caspian in Turkmenistan. Nearly 920 animal species live in the Caspian Sea. There are 79 species of vertebrates live here. In addition there are 101 other fish species in the Caspian Sea. They are Caspian Sea sturgeon, stellate sevruga, rock fish, white goldfish, salmon, five species of the Caspian herring, omul, chub and other species of fish.
They are found mainly in areas of rivers flowing into seas and are rarely in the sea.
1809 species and subspecies of animals live in the Caspian Sea, from them 1069 free-living invertebrates, 325 species of parasites and 415 species of vertebrate animals. Free-living animals are divided in five groups according to the origin in the Caspian Sea, and its testify that sea has a complicated history.
The Caspian seal is the only animal species of the Caspian Sea.
Fish in the Caspian Sea:
Sturgeon:
1. Bolga
3. Kur (Iran) sturgeon
4. Kalamo
5. Kur (the Southern Caspian Sea)long nosed
6. Herrings
1. Anchous flock
2. Big-eyed flock
3. Standard flock
4. Salmon
5. Lamprey
6. Caspian big-belled
7. Big-eyed herring
8. Volga herring
9. Black back herring
Chaki species
1. Omul
Mullets
2. Golden gray mullet
3. Round nosed mullet
Bullheads
1. Caspian bullhead
2. Round bullhead
3. Shirman bullhead
4. Sandy bullhead
5. Kessler bullhead
6. Knipovich bullhead
7. Grimm scoop bullhead
Other species
1. Atherina
2.Thread fish
Flora
The flora of the Caspian Sea consists of 755 species and sub-species, from which 5 is high plants. High plants grow in the lands, seas and fresh waters. These plants grow in the Caspian Sea: sea-grass, comb type water flower, 2 types of ruppia. High plants are feed for fished and water birds, too. Many fishes lay their caviar on them.
In phytoplankton of the Caspian Sea both fresh water and saline water algae lives. This is due to the lack of salinity of sea. In the phytoplankton of the Caspian Sea 450 species of algae have been recorded: 163 species of them is diatom algae, 102 species - blue-green algae, 139 species - green algae, 39 species - dinofit algae, 2 species - golden algae, 5 species - evglen algae. There are 47 species of seaweed, 66 species of water algae, 74 species of saltish - fresh water algae, 210 species of fresh water algae and 52 species of other algae in phytoplankton of the Caspian Sea.
Oil and gas reserves of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea has large volumes of hydrocarbon resources. According to various estimates, the Caspian Sea oil reserves reach 200 billion barrels. In addition, there are significant natural gas reserves in the sea. The surrounding states and foreign corporations actively participate in extraction of hydrocarbon reserves in the Caspian Sea. Today the Caspian Sea is one of region in the world, which plays a key role in energy security. Energy resources produced in the Caspian Sea play an important role in the development of the coastal countries and as well as the adjacent countries of the region.
The Caspian apart being important transportation hub and the factor in cleanness of the environment and air, has valuable natural fields. The main wealth of the Caspian Sea is oil and gas. The contract concluded in in September 20, 1994 with concern of the western states called later as Contract of the Century. The research shows that the Caspian is the largest oil reservoir in the world. At present, 67% of the oil produced in Azerbaijan, and 95% of gas is from the Caspian Sea.
To the east of Absheron Peninsula, in oil-rich region of the sea at depth of 100 meters more than 100 metal islands were built. The total length of piers is more than 400 km. Multistored houses and public buildings were build on piers, and the settlement established here is called Oil Rocks .
The Caspian coats is rich with beaches.
Sandy beaches of the Caspian Sea (in particular the coast of Baku) are suitable for the resort-tourism complex. These are among the 1001 Night, Aqua Park Shiлhov, Iceberg beach, Eldorado Beach (Shikhov), Amburan Beach Club (Bilgah), Barbados beach, Palm Beach (Novkhani), Beluqa (Buzovna), Black Jack Beach , Gilan Beach , Fras recreation center of the beach (whose), Pearl Beach , Sherlock\'s beach (Zagulba), etc. recreation areas are considered to be the most beautiful beaches in the summer season.
|
